Introduction for Automotive OEMs & Tier-1 Suppliers
As global EV adoption accelerates, the demands placed on the polymer systems that protect battery modules, BMS electronics, and high-voltage components have entered a new era of complexity. EV battery systems are now expected to maintain high thermal efficiency, withstand vibration and chemical exposure, deliver high-voltage electrical insulation, and increasingly contribute to thermal runaway mitigation (TRM).
The below information provides a distilled, engineering-grounded overview of the material classes available for potting and encapsulation, the selection criteria that matter most for high-volume and premium EV programs, and the performance trade-offs critical to component durability and pack-level safety.
ITW Performance Polymers’ advanced material portfolio, including high-reliability offerings such as Insulcast® potting and encapsulation products, aligns precisely with market needs for improved thermal management, mechanical protection, production throughput, and field reliability.
Why Potting & Encapsulation Have Become Foundational in EV Battery Engineering
Modern EV packs contain dozens of interdependent components that operate under severe and dynamic conditions:
- Persistent thermal loads from cells and power electronics
- Vibration and shock across vehicle lifetime
- Exposure to coolant, road contamination, salt, and humidity
- High-voltage electrical stress (400-800 V and trending toward 900-1000 V)
- Increasing regulatory demands for thermal runaway propagation resistance
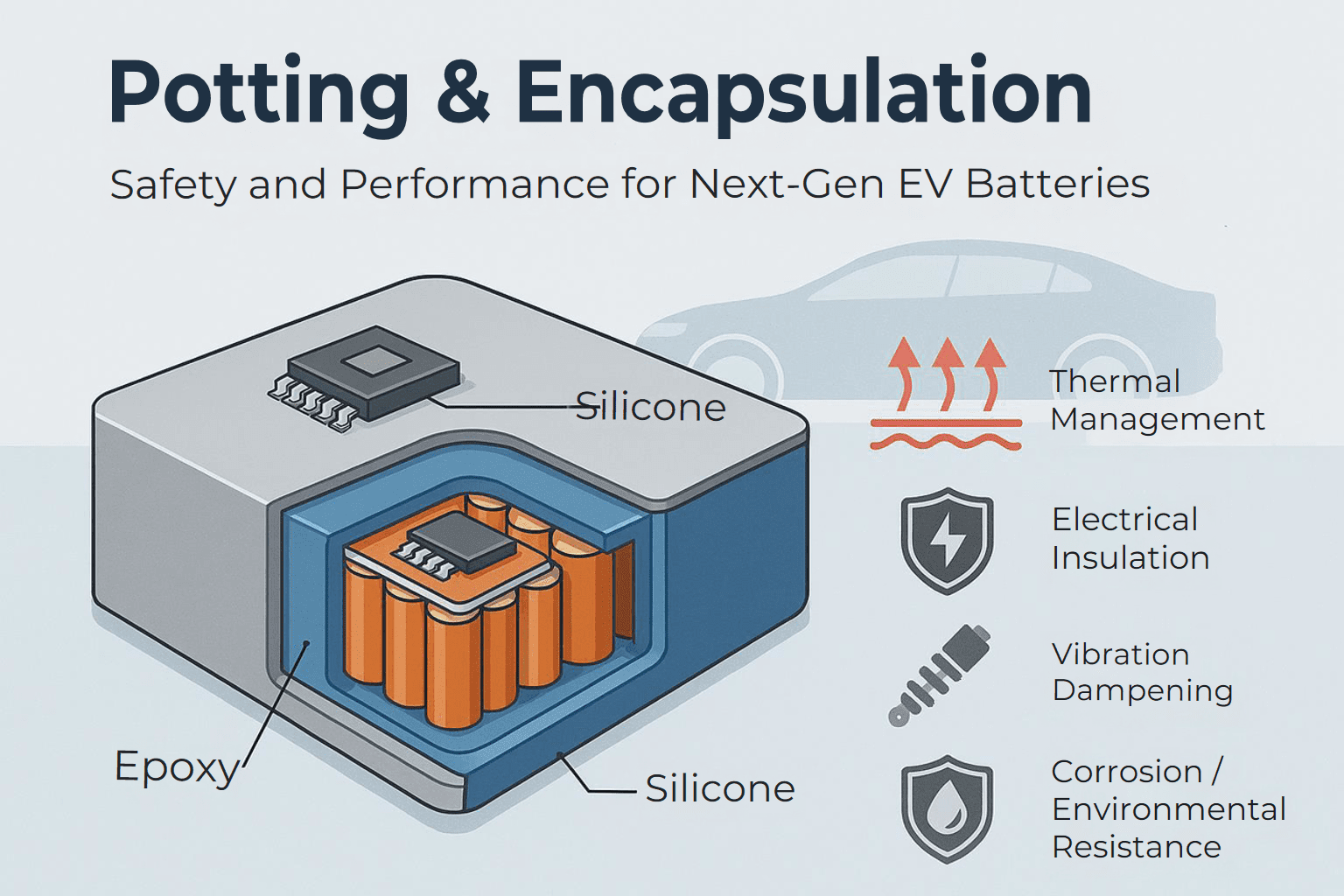
Potting and encapsulation materials are now critical enablers of performance and safety. They address five engineering priorities that directly influence pack durability and warranty risk:
Thermal Management
Efficient conduction away from hot zones, reduced thermal gradients, and improved thermal spreading across modules.
Electrical Insulation
Reliable dielectric barriers preventing arcing, HV tracking, and PCB failures—particularly essential for the next generation of high-voltage systems.
Mechanical Stability & Vibration Dampening
Protection of cell welds, PCBs, connectors, and busbars across millions of vibration cycles.
Environmental & Chemical Resistance
Defense against moisture, glycol-based coolants, road salt, dust, and electrolyte leakage.
Thermal Runaway Mitigation (TRM)
Materials with high heat capacity, controlled expansion, and fire resistance help delay or limit propagation.
Where Potting & Encapsulation Matter Inside the Battery System
Potting and encapsulation play targeted roles across multiple subsystems:
- Battery modules: Gap-filling between cells, insulation around busbars, conduction to cold plates
- High-voltage components: Busbar potting, HV connector sealing, current sensor encapsulation
- BMS electronics: PCB protection, vibration stabilization, heat dissipation for power FETs
- Pack-level barriers: Thermal shields and TRM layers that isolate modules
Each use case has distinct thermal, mechanical, and dielectric constraints—reinforcing that material selection must be intentional, not generalized.
Overview of Material Classes & Their Ideal Applications
EV battery programs typically utilize four polymer families, each with strengths tied to the engineering problem they solve.
- Polyurethane (PU) & Hybrid
Best for: BMS assemblies, pouch modules, complex geometries needing flow
Advantages:
- Low exotherm (critical for sensitive cells)
- Excellent vibration damping
- Lightweight for range optimization
- Substrate compatibilities
- Epoxy
Best for: High-voltage insulation, structural reinforcement, harsh environment duty cycles
Advantages:
- High adhesion and mechanical strength
- Superior dielectric performance
- High chemical resistance
- High thermal conductivity options for demanding heat-flux zones
- Silicone
Best for: Removability/error mitigation, high-expansion zones, TRP layers
Advantages:
- Exceptional temperature stability
- Very low modulus – ideal for expansion zones
- Excellent fire resistance and aging behavior
- High thermal conductivity options
4. Acrylic
Best for: Ultra-high-speed production lines
Advantages:
- Extremely fast cure (seconds to minutes)
- Good adhesion
- Attractive cost profile for volume programs
EV Battery Material Comparison Matrix
(Condensed representation of full dataset)
- Thermal conductivity ranges: 0.3–3.5 W/mK
- Operating temperature windows: –50°C to 200°C
- Dielectric strength benchmarks: 10–25 kV/mm
- Modulus options: from very soft (silicone) to rigid (epoxy)
- Cure speeds: from seconds (acrylics) to <10 minutes (PU & Hybrid)
- Cost tiers: PU ($), Acrylic/Hybrid ($$), Epoxy ($$), Silicone ($$$)
This landscape underscores that the “right” material is one optimized for the intersection of cell format, pack architecture, manufacturability, and safety objectives.
Engineering Criteria for Material Selection
Thermal Performance Requirements
- ≥0.8 W/mK for standard duty
- ≥1.5 W/mK for high-power modules and dense layouts
- Low exotherm for deep potting volumes
Electrical Insulation Targets
- Dielectric strength ≥15 kV/mm for 400–800 V systems
- Volume resistivity ≥10¹⁴ Ω·cm
Mechanical and Vibration Considerations
The optimal modulus depends on cell architecture:
- Cylindrical: Higher modulus → epoxy or silicone
- Prismatic: Flexible → silicone or soft PU
- Pouch: Ultra-low pressure → low-modulus PU or gels
Environmental Durability
Materials must resist:
- Coolant exposure
- Salt spray & humidity
- Electrolyte leakage
- Thermal cycling (ISO 16750)
Water absorption should remain <1.0%.
Manufacturing Fit & Throughput
- Cure times <10 minutes ideal for high-volume automation
- Robot-friendly viscosities and long pot life
- Simple mix ratios (1:1 or 2:1) optimize process reliability
Application-Specific Recommendations
- Cylindrical Packs (2170/4680)
High heat flux + structural rigidity
Recommended: High-TC epoxy or silicone
- Prismatic Packs
Expansion-driven mechanical stresses
Recommended: Flexible silicone or soft PU
- Pouch Packs
Pressure-sensitive, thermally dynamic
Recommended: Low-modulus PU or gel
- BMS and Power Electronics
Electrical insulation + chemical durability
Recommended: Epoxy or silicone
Customer Benefits from High-Performance Polymer Systems
- Enhanced safety through improved TRM delay
- Prolonged battery longevity via reduced thermal gradients
- Higher reliability under humidity, coolant contact, and vibration
- Lower warranty costs from stabilized electronics and minimized failures
- Faster, more repeatable manufacturing cycles
ITW Performance Polymers: Technology Positioned for the Next Generation of EV Platforms
ITW Performance Polymers has been a long-standing materials innovator serving automotive, electronics, and industrial markets. Our formulations are engineered for reliability, manufacturability, and safety: three pillars that OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers consistently rank as top priorities.
Within our advanced polymer lineup, the Insulcast family represents a standout solution for EV battery electronics and high-voltage subsystems. Designed for robust dielectric protection, stable thermal performance, and compatibility with automated dispensing, Insulcast aligns closely with the selection criteria described in this paper—making it a natural fit for BMS potting, HV encapsulation, and TRM-supportive designs.
While this document is material-agnostic for engineering clarity, programs that require balanced electrical insulation, low exotherm, and process-stable viscosity often find Insulcast formulations to be a best-fit candidate.
Conclusion
The EV sector is moving quickly toward higher energy densities, faster charging, and tighter packaging constraints. As a result, potting and encapsulation materials have become strategic components, not commodities, within battery pack engineering.
Selecting the optimal material system requires a holistic evaluation of thermal performance, electrical properties, mechanical fit, environmental durability, manufacturability, and cost.
With decades of deep polymer expertise and a portfolio that includes high-performance systems such as Insulcast, ITW Performance Polymers is positioned to support OEM and Tier-1 teams seeking safer, more durable, and more efficient EV battery solutions.
By: Andrew Kastner, Product Manager
View all our Technical Data Sheets and Safety Data Sheets. Need some help? Ask a technical question and find a solution!
For more information like this, follow ITW Performance Polymers on LinkedIn and sign up for enewsletter in our website footer.

